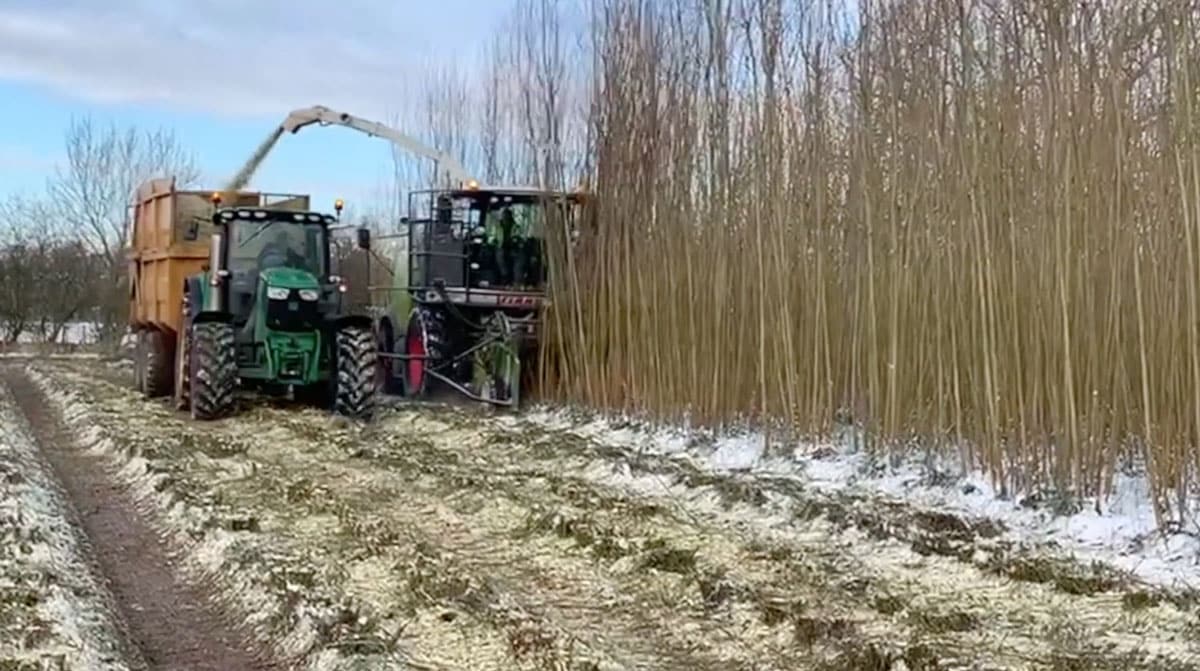
Black Locust
Robinia pseudoacacia
General info
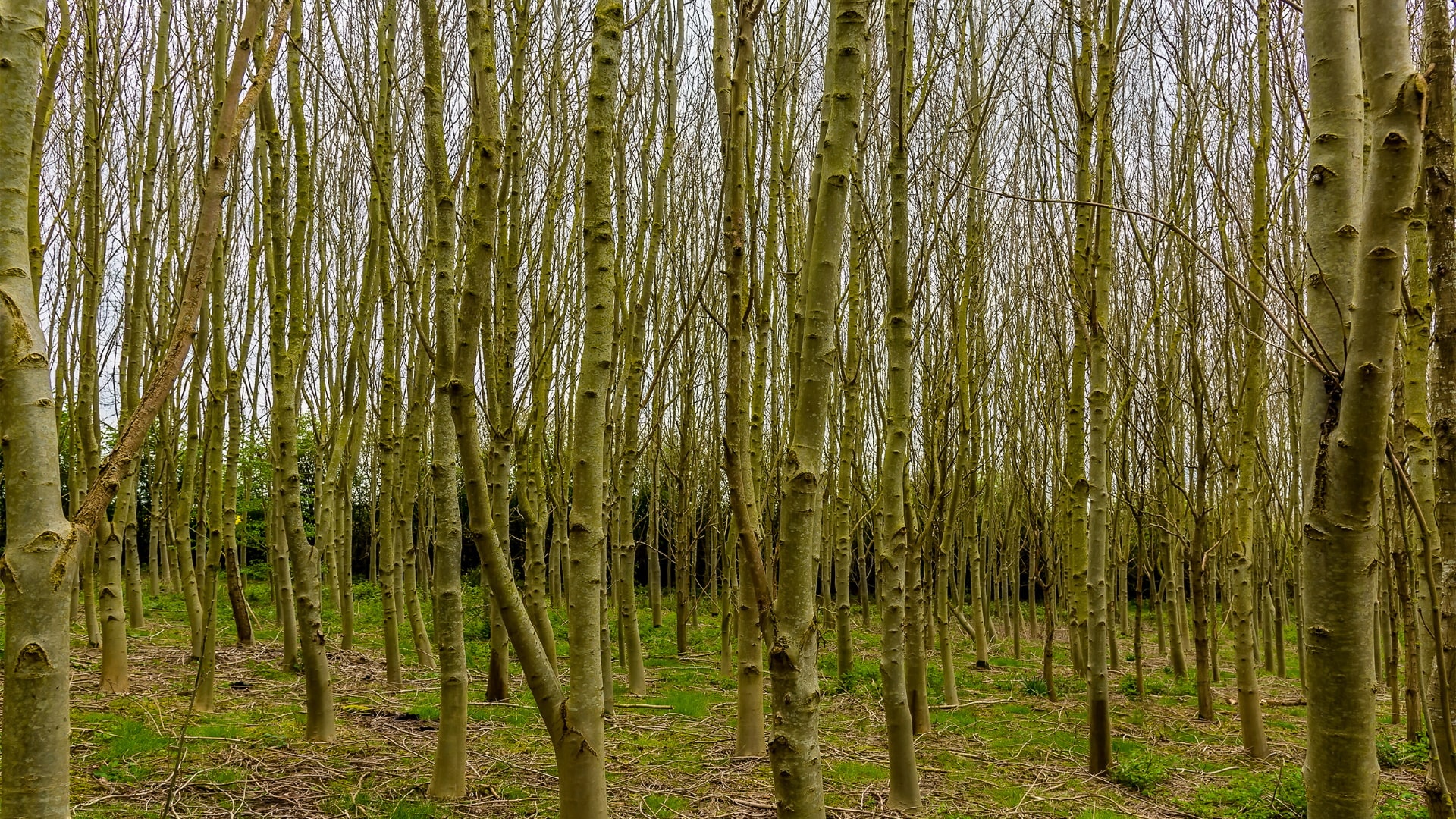
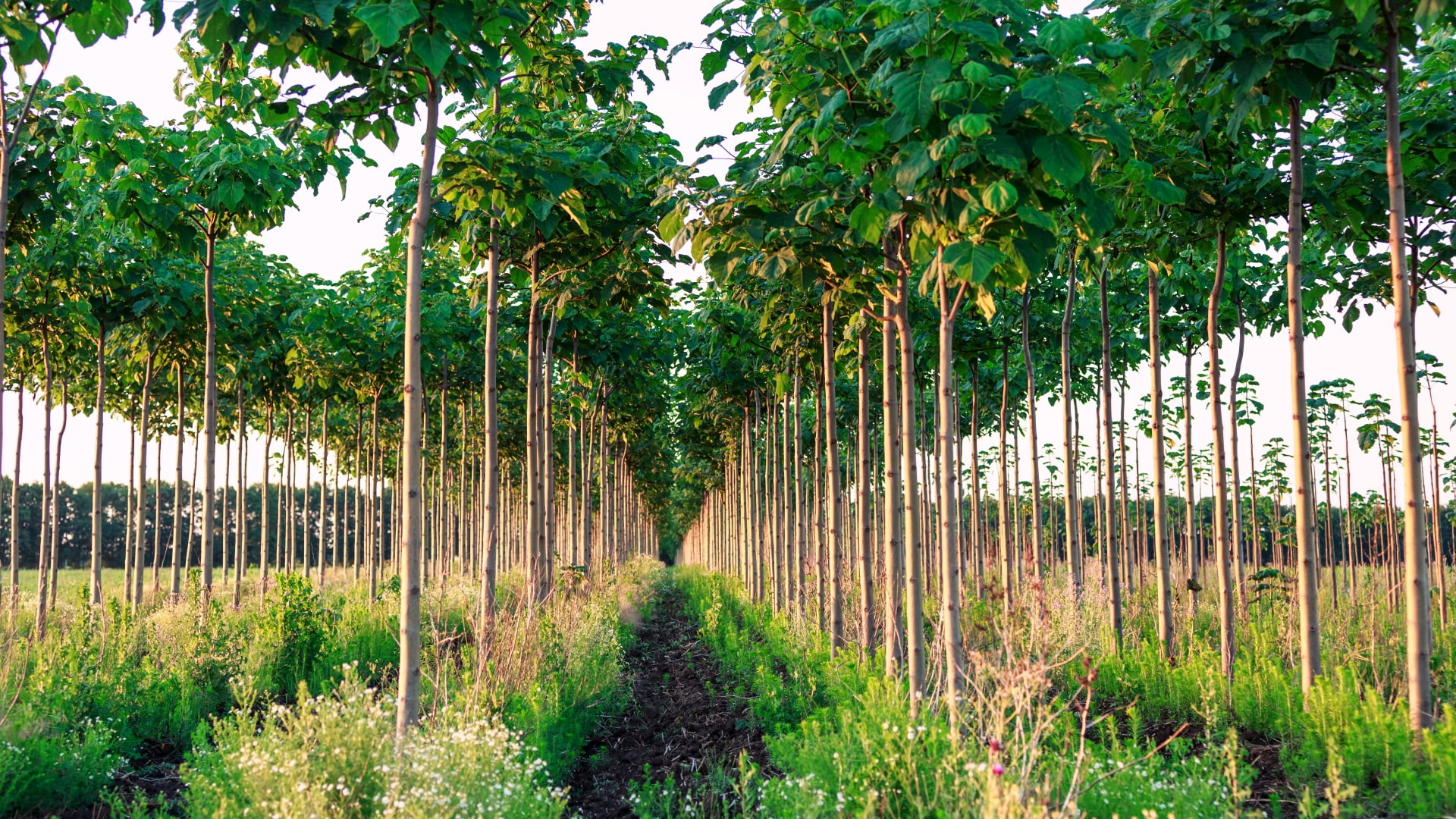
Black locust is a medium-sized hardwood deciduous nitrogen-fixing tree. The tree is native to a small region in southern United States, but it has been transplanted across the globe in temperate and sub-tropical regions. Black Locust is one of the most commonly planted commercial hardwood trees with an estimated 2.5 million ha in lumber and energy production globally. In Hungry, black locust account for over 20 percent of forested land.
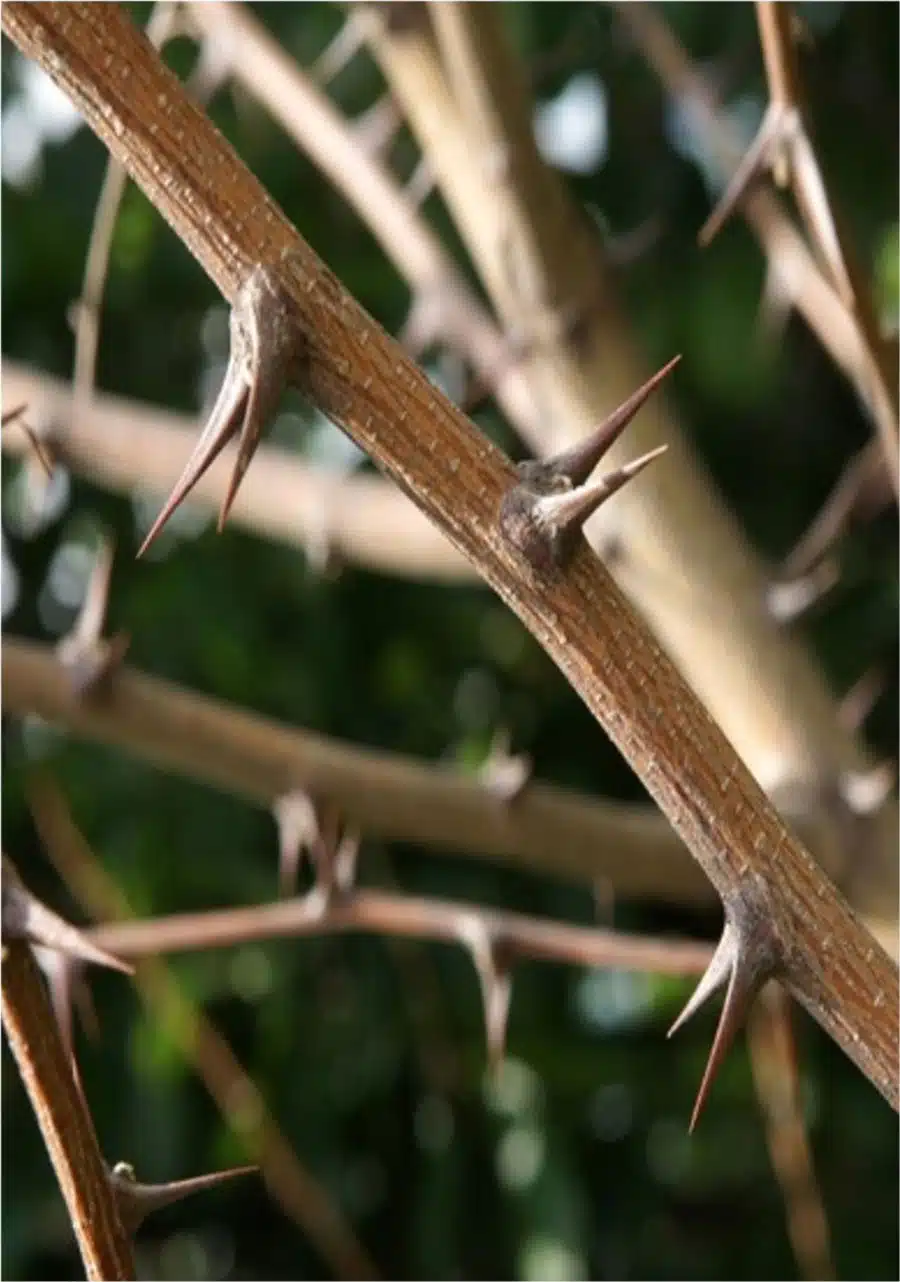
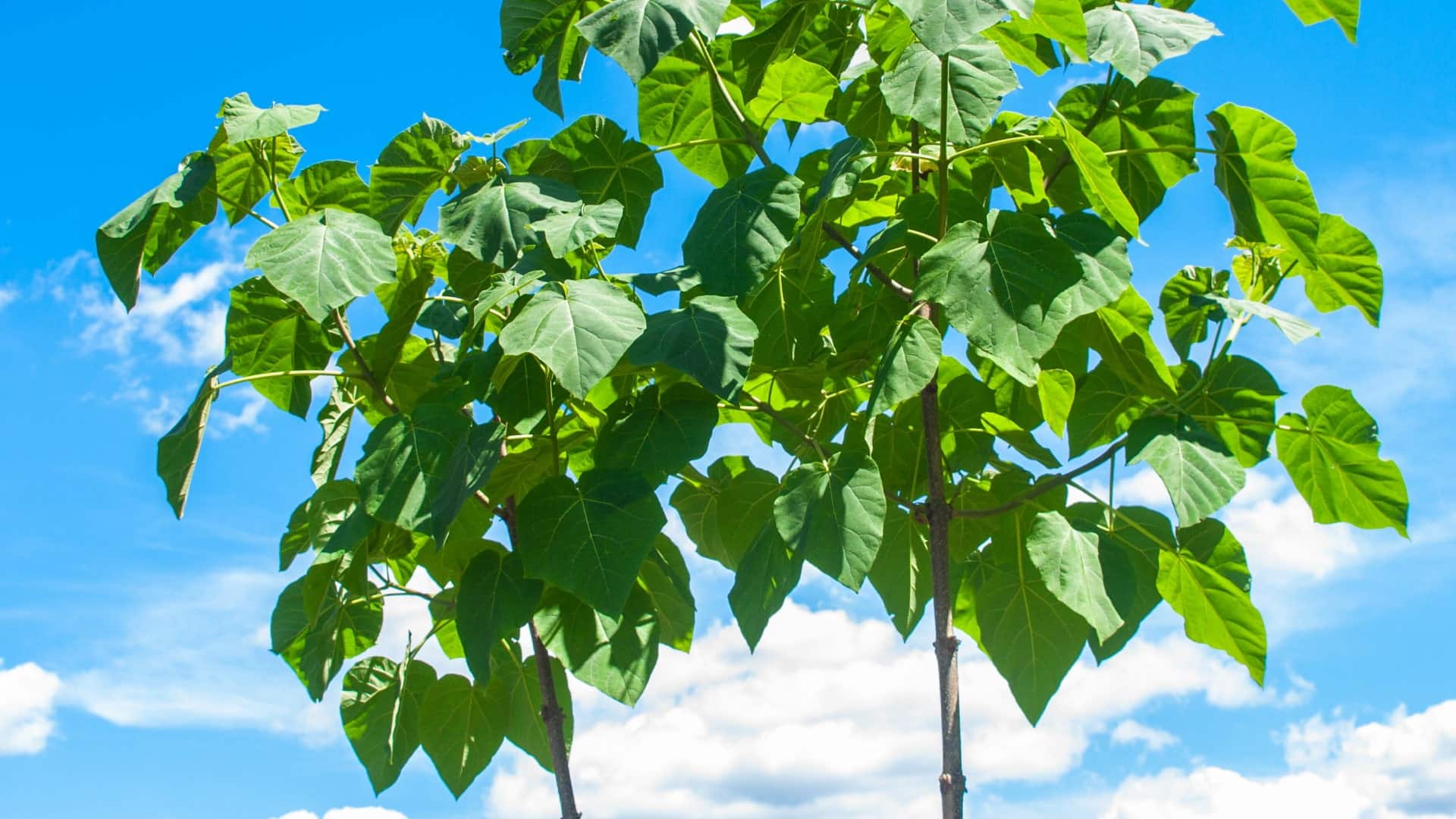
Black locust is a fast-growing tree, often growing to a height of between 12 to 30 meters high depending on the cultivar. It has pinnately compound leaves of 6 to 14 inches long that are alternately arranged along short branches. Each leaf includes 7 to 19 leaflets that are 1 to 2 inches long and has an open canopy structure. The leaves are dark blue-green in summer and turns yellow-green in fall. Depending on the cultivar, some trees have thorns at the base of the leaves.
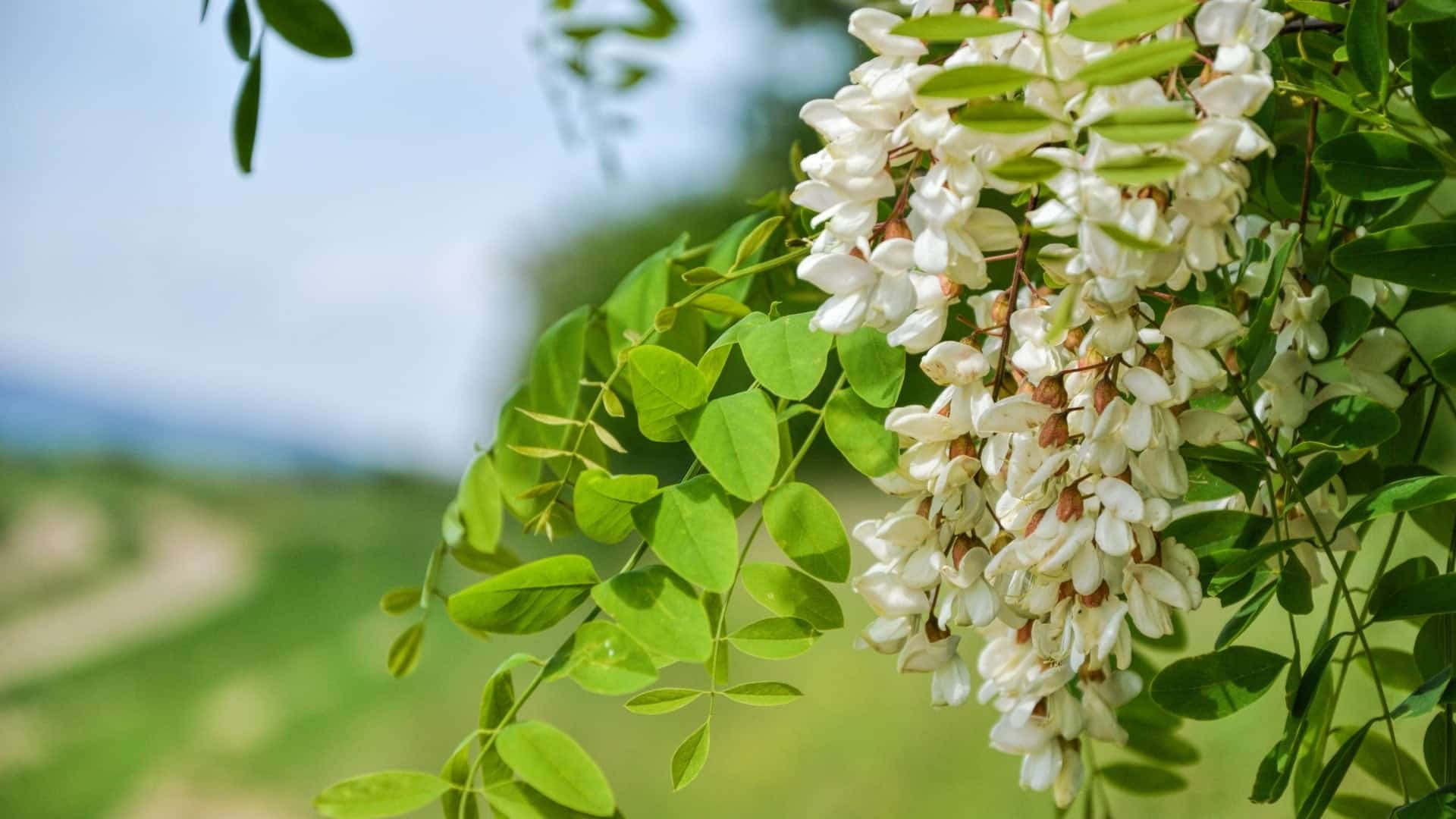
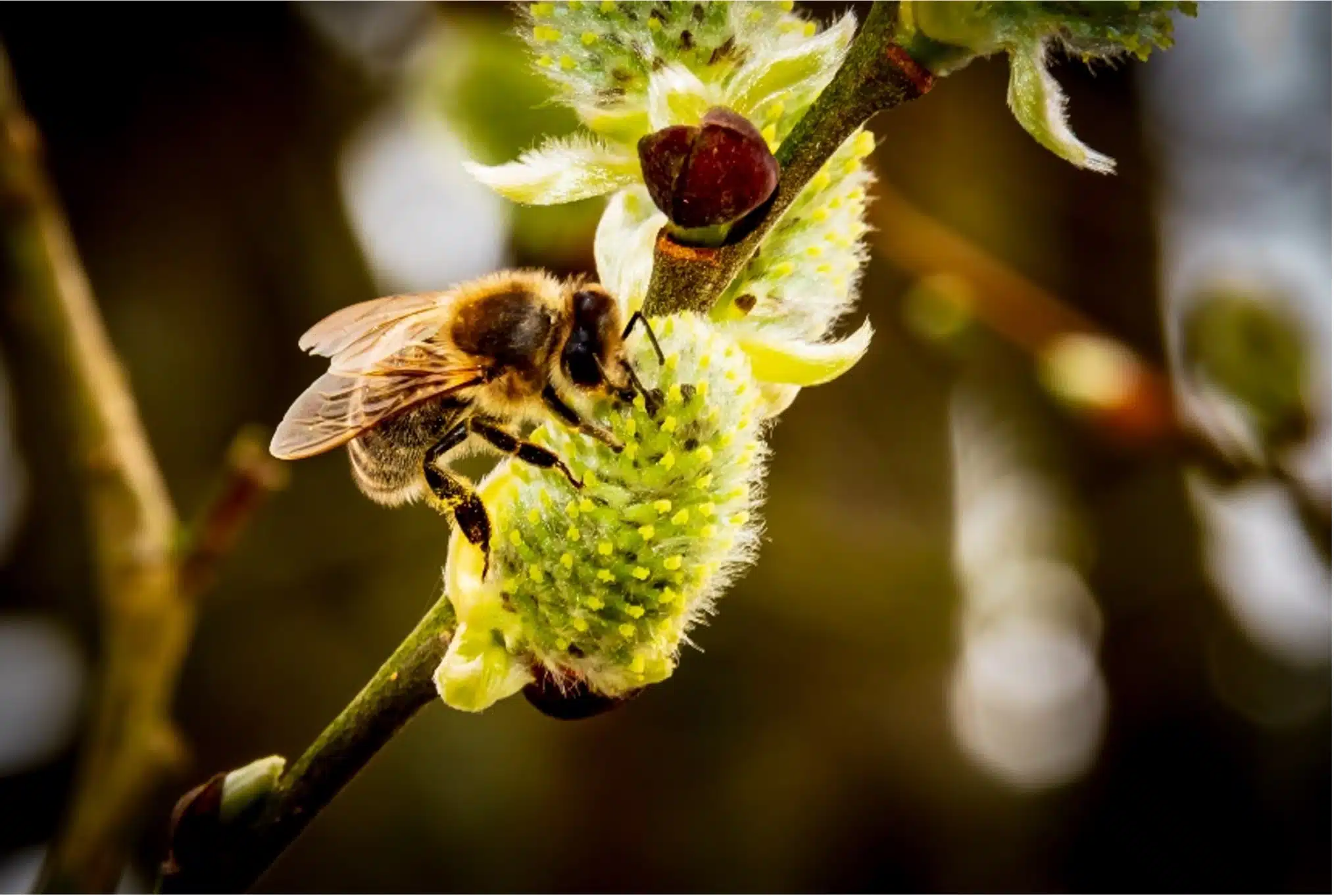
The tree produces large white or rose-pink flowers which appear in large dense cluster on the tree and produces a powerful fragrance. The flowers attract honeybees in late spring providing a nectar resource for pollinators. The honeybees in return pollinate the tree.
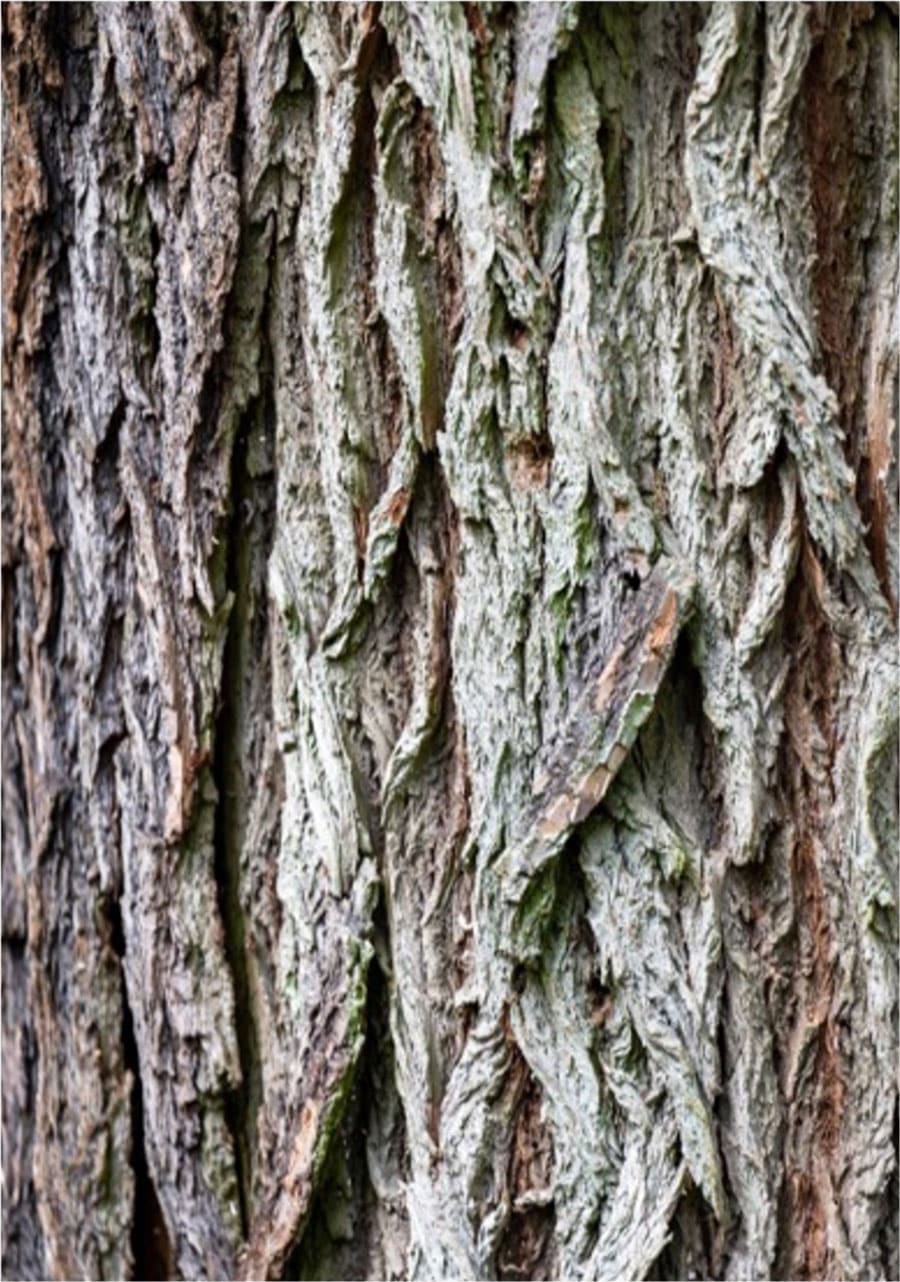
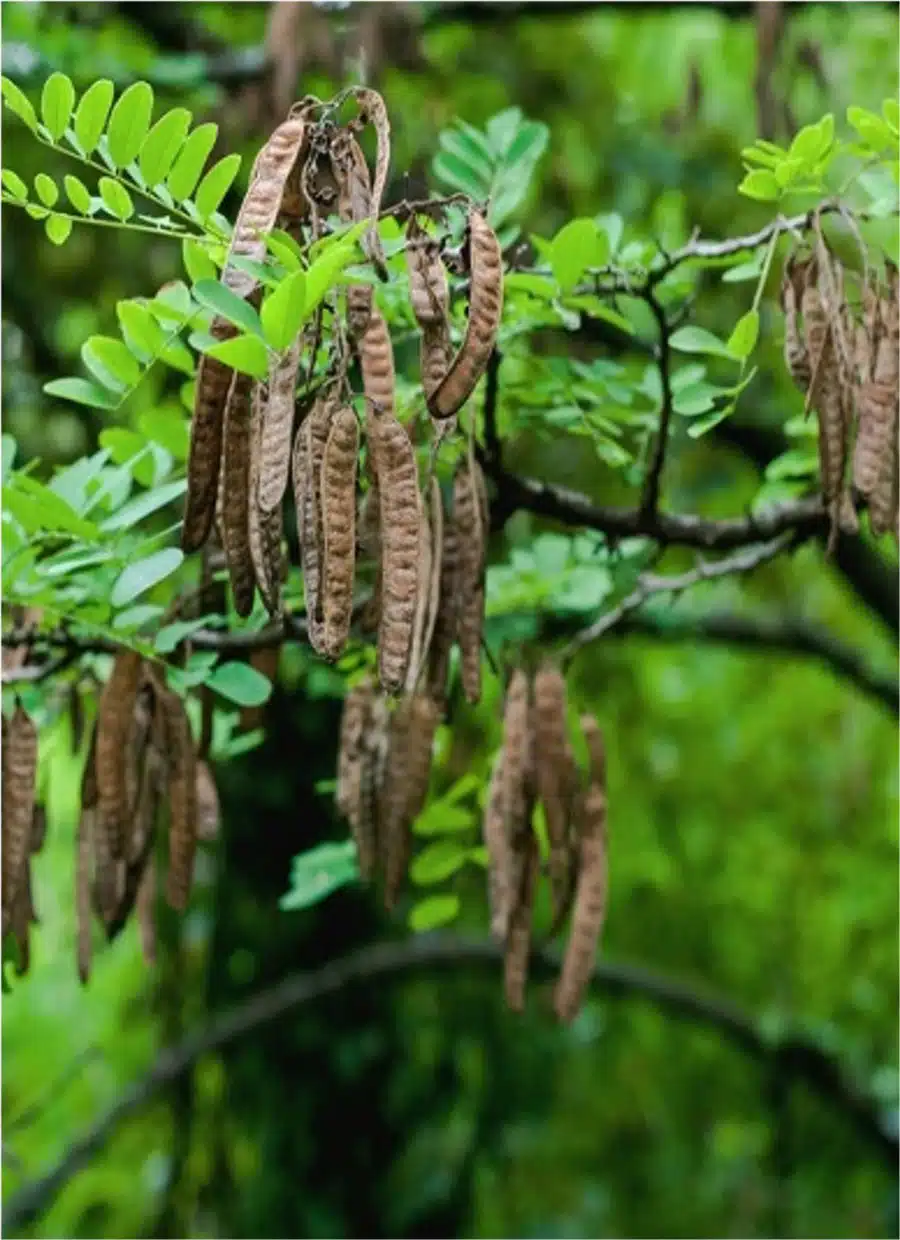
Black locust produces pea-like fruit pods of 5 to 10 cm long and 1-2 cm wide which usually contains about 4 to 8 seeds. The seeds mature in autumn and persist through winter until early spring. The trunk is usually black and grey and has many deeply furrowed ridges and grooves that forms diamond shapes. The roots have nitrogen fixing nodules, meaning the tree has limited fertiliser requirements.
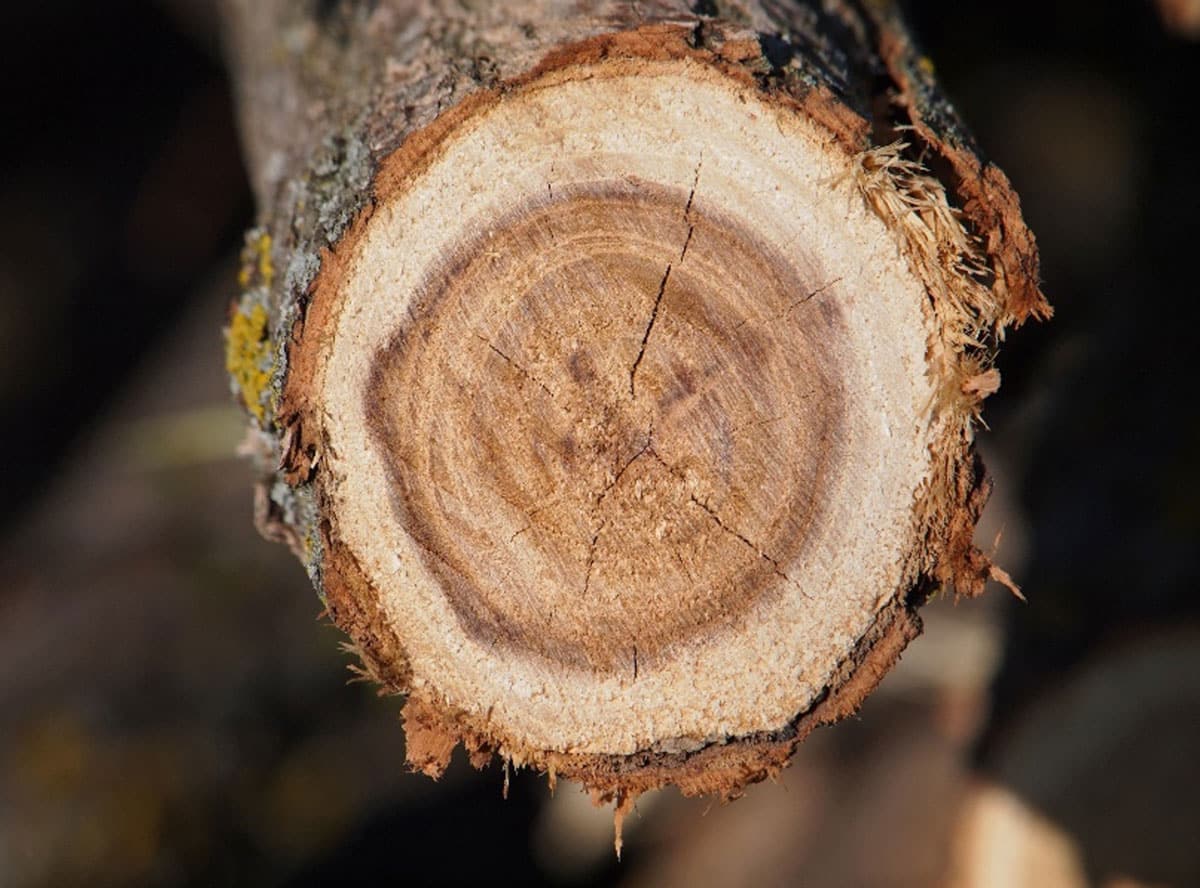
The wood from black locust is one of the hardest woods worldwide. It is pale yellowish brown, dense, hard, durable, and resistant to rot.
Invasiveness of Black Locust
Black locust is considered an invasive species. And is classified as one of the top 100 woody invaders worldwide. It can quickly colonise, out competing other species of trees and shading out competitors. The suckering roots of black locust spread quickly and form many suckers resprouting into new shoots. Black locust shed its seeds and spread to establish new seedlings. The seeds can remain dormant for close to 10 years.
Farmers should consider monitoring the spread of the black locust seeds and suckers outside the planted location to minimize seedling establishment. The spread of black locust can to a limited extent on small scale be controlled by hand pulling, mowing, constantly removing the suckers from both the roots of the trees and from the trunk to minimize regrowth. However, these methods may not completely eradicate the establishment of seeds.
Site Suitability
Black locust is a good pioneer species which is shade intolerant and requires a lot of sun. Black locust thrives in moist loamy well drained soils but can tolerate dry nutrient poor soils also. It can tolerate a range of pH’s across European plantations (3.2–8.8) with an optimum range of 5.5–7.0. Optimum conditions ensure the productivity of root-associated nitrogen fixing bacteria, which can help to fix between 75–150 kg of N ha-1 yr-1. It can tolerate a range of altitudes, though it grows best between 600–700m above sea level.
Establishment and management
Black locust can be propagated by seed, root, or stem cuttings. When planting by seed, boiling water or sulfuric acid treatment will be required due to the hard seed coat. Plant black locust between November and March.
Black locust is fast growing producing large amounts of biomass which can be easily coppiced. The tree produces high-density wood which can be harvested and produced into pellets with high energy content.
Utilised normally on a 1–3-year rotation period, it can grow to heights of 10m within 5 years with coppice growth from stool shoots having been demonstrated maximums of 4.9m a year in certain studies. The volume growth from coppice stands has been shown to range between 10 – 16 m3 ha-1 y-1 as early as 5–10 years into cycles. However, over time, if regeneration of stands is performed from stool shoots, a decreasing trend of wood production is observed, necessitating the need for regenerating plantations via seed or root sucker alternatives periodically. This leads to many strategies currently employing 2–3 coppice cycles, or at most 5 cycles in some studies, before stools are removed and replanted from other sources.
The yield of black locust varies according to location, harvest timing, and agronomic practices. A study in Hungry reported average yield of 6.5 Mg ha-1 yr-1 at dense spacing of 22,000 plants per hectare on a 5-year for cultivars such as Üllői, Nyírségi, Jászkiséri, Kiscsalai.
Pests and diseases
The most common pest is the black locust borer (Megacyllene robiniae). The larvae burrow into and weaken the tree’s trunk and branches. Although black locust can survive locust borer attack, the damage causes stunted growth and internal decay which makes the tree more susceptible to breaking apart in very windy conditions.
The locust leaf miner (Odontota dorsalis) and the black locust gall midge (Obolodiplosis robiniae) are another main pest which affects black locust. The locust leaf miner causes the leaves to turn brown in the summer. The black locust gall midge causes gall formation and premature leaf drop. Other insect pest includes the sawfly larvae, bag worms, leaf and tree hoppers, aphids, and carpenter moths.
Although black locust has many pests and insects, many of these diseases seldomly kill the tree. Fortunately, the main pests – black locust borer and locust leaf miner – is not yet present in the UK.
Insecticide treatment may be required for treating pest and disease infestation, however, maintaining good growing conditions, and preventing insect attack is essential especially during the first one to three years of growth. Interplanting with other species may reduce susceptibility to pest and disease attacks.
Benefits and uses of Black Locust
- Soil improvement: Black locust is able to fix nitrogen which is ultimately returned to the soil. This increases the presence of nitrate, ammonium in the soil.
- Reclaiming/rehabilitating degraded soils: When grown on marginal lands with low soil fertility it has the potential to improve soil fertility due to its ability to fix atmospheric nitrogen. Black locust has been used in mine reclamation in Germany and in reclaiming degraded lands in Romania.
- Prevention of soil erosion: Its extensive root system and prolific suckering can prevent soil erosion, and on previously eroded soils increase soil porosity, soil organic matter, nitrogen, and phosphorus.
- Source of food for pollinators: The flowers are important source of food for honeybees, leading to the production of high-quality honey.
- Improve biodiversity: Black locust is fast growing tree and host to many species of insects, mammals, and birds.
- Windbreaks and shelterbelts: Black locust is used as windbreaks, shelterbelts, shade and shelters for animals in silvopasture grazing systems.
- Hard wood: The wood from black locust is one of the hardest wood and is highly rot resistant, making it an ideal material for fenceposts, poles, furniture, wooden panelling, flooring and firewood.
- Raw material for other products: Black locust is used as raw material in biotherapy, apiculture, food industry, landscaping, and many other products.
Return to crops overview
Relevant research
Straker, K. C., Quinn, L. D., Voigt, T. B., Lee, D. K., & Kling, G. J. (2015). Black locust as a bioenergy feedstock: a review. Bioenergy Research, 8(3), 1117-1135.
Nicolescu, V. N., Rédei, K., Mason, W. L., Vor, T., Pöetzelsberger, E., Bastien, J. C., … & Pástor, M. (2020). Ecology, growth and management of black locust (Robinia pseudoacacia L.), a non-native species integrated into European forests. Journal of forestry research, 31(4), 1081-1101.
Biomass Connect Trials
Black Locust ‘Turbo’ and Black Locust ‘Turbo Obelisk’ varieties are currently being grown as part of the Biomass Connect trials at the following hub sites:
- AFBI Hillsborough
- BGI Chesham
- IBERS Aberystwyth
- NIAB Headley Hall
- Newcastle University Cockle Park Farm
- Rothamsted Research North Wyke
- SRUC Ayrshire
- SRUC Edinburgh
Common Alder
Alnus glutinosa
Other short rotation forestry species include ‘Italian’, ‘Green’ & ‘Red’ alders
General info
Native to the UK, common alder is a water loving tree that grows well in swampy areas or close to rivers, lakes and ponds, with root structures that provide support toward prevention of soil erosion in these areas. The wood produced from this species isn’t as susceptible to rotting when waterlogged and has historically played roles in underwater construction and boat building. Alder forms associations with bacterium Frankia alni, allowing it to thrive in lower nutrient soils, and within the genus Alnus there are 30 species. Common alder is a monoecious species with both male and female catkins found on the same tree. They undergo wind-pollination and seeds are distributed by wind and water on maturation.
A notable current risk for this species is the discovery of a hybrid strain of Phytophthora, which can cause alder dieback, when previously it was assumed that alder was not impacted by these fungi significantly. Alder is also suggested to have medicinal properties within the bark and seeds with possible interesting antioxidant and antimicrobial activities. It may be suitable for both short rotation forestry due to its relatively significant growth levels in the first 10-15 years and is amenable to coppicing regrowth with the coppice quality being most suitable for bioenergy biomass utilisation.
Cultivation and agronomy
Common alder grows well in all soil types but requires significant moisture levels and does not grow well at higher elevations. The leaves lack mechanisms for controlling transpiration and this in part is a large factor relating to their water-demanding nature. They are tolerant of a range of temperatures, growing well across both northern and southern Europe.
They can reproduce via seed which following maturation (age 3–30 depending on ecotype) they produce every 3–4 years but new seed germination requires light levels that are generally unachievable under a mature stands canopy. The seeds of the alder species can float on water and remain viable in this situation for around a year. Successful germination is reliant on higher humidities.
Other alder species have different tolerances with ‘Italian’ and ‘Green’ alders needing less water whilst ‘Red’ alder does not do well on dry or sandy sites. They have yields averaging 4–14 m3 ha-1 y-1 with a normal rotation length of 35-50 years across species when not harvested on a SRF system. They grow at a rate of up to 1.5 m a year between peak ages of 4 to 10 years old before slowing and max heights fall around 28.5 m tall (between ages 50-80).
Where yield is concerned the annual volume increment reaches maximum around the 20-year age mark achieving 13–18 m3 ha-1 y-1. Alder is also noted as having potential as a coppicing species particularly in mixed systems where alder can offer the co-benefits associated with its nitrogen fixation abilities to boost co-localised species growth patterns.
Return to crops overview
Relevant research
Claessens, H., Oosterbaan, A., Savill, P., & RONDEux, J. (2010). A review of the characteristics of black alder (Alnus glutinosa (L.) Gaertn.) and their implications for silvicultural practices. Forestry, 83(2), 163-175.
Dahija, S., Čakar, J., Vidic, D., Maksimović, M., & Parić, A. (2014). Total phenolic and flavonoid contents, antioxidant and antimicrobial activities of Alnus glutinosa (L.) Gaertn., Alnus incana (L.) Moench and Alnus viridis (Chaix) DC. extracts. Natural product research, 28(24), 2317-2320.
Biomass Connect Trials
SRF Alder is currently being grown as part of the Biomass Connect trials at the following hub sites:
- AFBI Hillsborough
- BGI Chesham
- IBERS Aberystwyth
- NIAB Headley Hall
- Newcastle University Cockle Park Farm
- Rothamsted Research North Wyke
- SRUC Ayrshire
- SRUC Edinburgh
Eucalyptus
Eucalyptus nitens, Eucalyptus gunnii, Eucalyptus urnigera, Eucalyptus dalrympleana, Eucalyptus glaucescens, Eucalyptus rodwayi, Eucalyptus globulus
General info
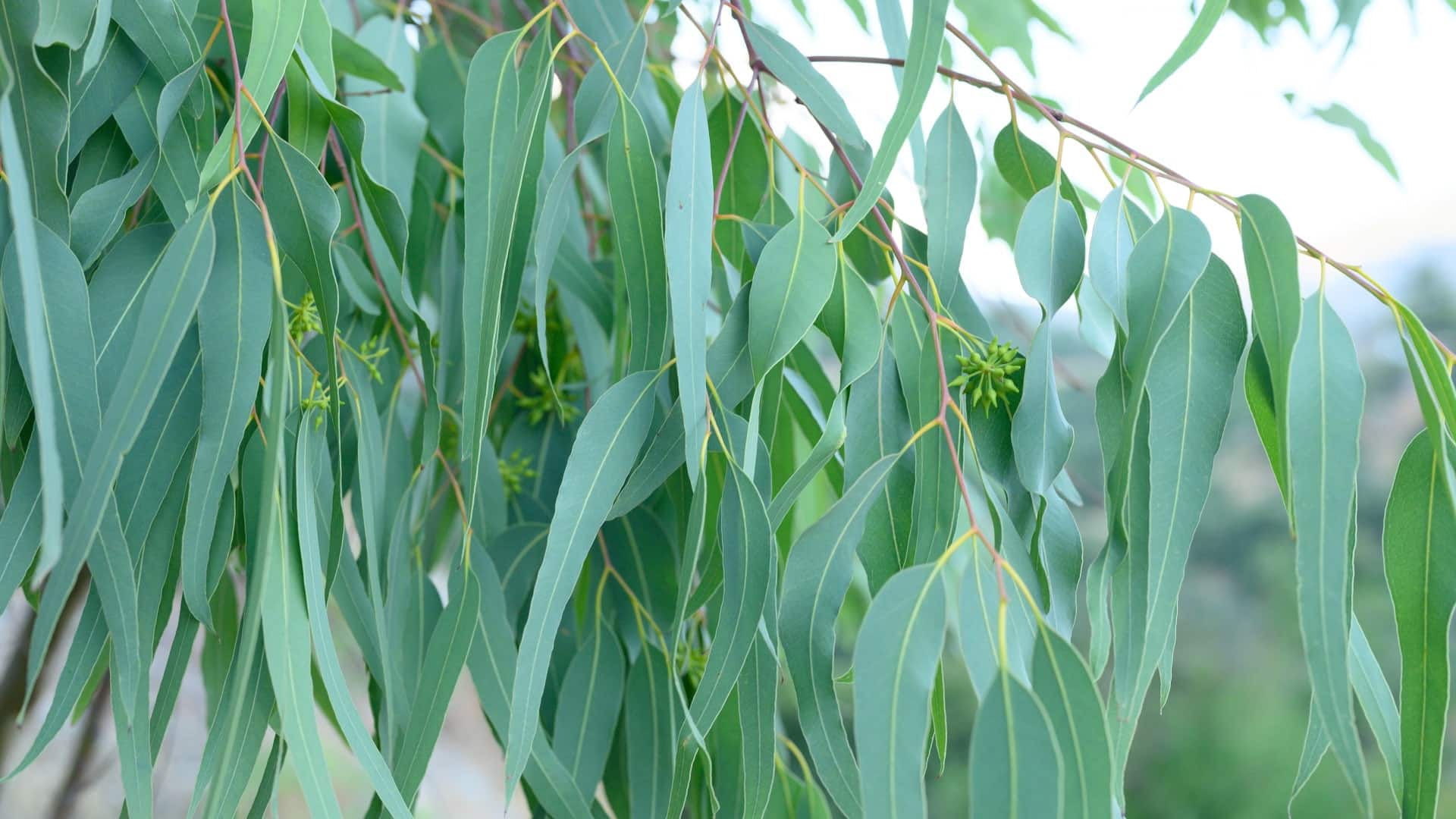
Eucalyptus is suited to short rotation forestry due to its fast growth rate and high biomass yield, which can exceed that of other native species. When planted in favourable locations, growth rate can be 2 – 3m per year and can be harvested from 4-6 years onward. Based on an 8-10 year rotation, data from UK trials identified yields in the range of 20-30 m3 ha/yr, on a bark-free basis, equivalent to 10-15 oven dry tonnes per hectare per year.
Eucalyptus produces a high-density wood, with a net calorific value of 18 GJ t, which seasons quickly and is suitable for use as a biomass fuel or timber product. Eucalyptus light canopy can afford options for growth in the understory. This means stands are well suited to agroforestry use (silvo-arable/pastural) as well as in shelterbelts, riparian buffer strips and sight screens.
Cultivation and agronomy
Planting is performed from seedlings at stocking densities of between 1,600-2,500 stems per hectare at 2.5 x 2.5m – 2.0 x 2.0 m spacing. 2-3 ha is considered the minimum area for viable commercial production. Tree shelters and stakes are generally required to protect young plants and support early growth. Due to rapid growth rates, close monitoring is essential for the first few years until trees successfully establish. Coppicing can be performed from years 2–7 and stools will be productive for 3-4 rotations of 4-8 years, after which stool viability drops.
Low temperatures and unseasonal temperature fluxes are the main limiting factor to Eucalyptus growth. Frost damage can be a problem during establishment, but risk can be mitigated by proper species selection and silvicultural management.
Few pests are currently prevalent in UK. Psyllids are a common infestation on establishing trees but generally have minimal impact. Eucalypts have displayed good resistance to Phytophthora and other foliar pathogens.
Return to crops overview
Relevant research
Purse, J. G., & Richardson, K. F. (2001). Short rotation single stem tree crops for energy in the UK-an examination with Eucalyptus. Aspects of applied biology, (65), 13-19.
Leslie, A., Mencuccini, M., Purse, J. G., & Perks, M. P. (2014). Results of a species trial of cold tolerant eucalypts in southwest England. Quarterly Journal of Forestry, 108(1), 18-18.
Leslie, A. D., Mencuccini, M., & Perks, M. P. (2018). Preliminary growth functions for Eucalyptus gunnii in the UK. Biomass and Bioenergy, 108, 464-469.
Leslie, A. D., Mencuccini, M., Perks, M. P., & Wilson, E. R. (2020). A review of the suitability of eucalypts for short rotation forestry for energy in the UK. New Forests, 51(1), 1-19.
Biomass Connect Trials
SRF Eucalyptus is currently being grown as part of the Biomass Connect trials at the following hub sites:
- AFBI Hillsborough
- BGI Chesham
- IBERS Aberystwyth
- NIAB Headley Hall
- Newcastle University Cockle Park Farm
- Rothamsted Research North Wyke
- SRUC Ayrshire
- SRUC Edinburgh
All of the sites above have the following 4 common species:
- Eucalyptus dalrympleana
- Eucalyptus gunnii
- Eucalyptus glaucescens
- Eucalyptus uringera
In addition, the more southerly sites at IBERS, BGI, North Wyke and AFBI in Northern Ireland also have:
- Eucalyptus nitens
The more northerly sites at SRUC Ayrshire, SRUC, Boghall, Cockle Park Farm and NIAB Headley Hall have:
- Eucalyptus denticulate (this is in place of Eucalyptus nitens which is not hardy enough for the northern sites)
Additional Resources from Biomass Connect

Read our Eucalyptus Technical Article

See our Eucalyptus Factsheet
Watch Bryan Elliott’s Biomass connect webinar: Eucalyptus as a short-rotation forestry crop for the UK
Paulownia
Paulowniaceae spp
General info
A hardwood tree genus encompassing 17 species native to China and East Asia. Noted as one of the fastest growing trees in the world, it is unsurprising that its potential as a bioenergy crop is of interest. Wild type species tend to utilise the C4 photosynthetic enzyme cycle being a key element towards their ability to gain biomass quickly, however, many more modern hybrids utilise the C3 enzyme cycle.
Paulownia produces a lightweight but strong timber which has been heavily used by Japanese craftsmen for decades for the construction of furniture and instruments. Its leaves and flowers are also known to be good sources of fat and sugar for fodder, and nitrogen for green manure, suggesting potential roles in agroforestry incorporation strategies.
Cultivation and agronomy
Paulownias require permeable soil with a pH value above 5 (5-8.9) and tend to grow best in temperatures between 15-16 °C though they have a range of tolerance between -25 and 47 °C depending on the species. In a growth review of this species in Europe, different species and hybrids demonstrated highly variable yields and wood qualities. Yields in the second year of cultivation studies ranged from 1.5-14 oven dried tonnes per hectare per year. Despite showing approximately equivalent energy profiles to both willow and poplar (~19 Mj/kg), there is debate over the quality of fuel pellets produced due to the low-density wood, with the resulting potential requirement for processes such as biomass torrefaction to produce better fuel quality.
Paulowniaceae spp are at risk during juvenile growth, due to the very large leaf size and lack of sufficiently woody stems early on. Plantations of these tree species are susceptible to high winds causing mechanical damage if windbreaks and protection are not in place. Paulowniaceae spp have shown comparable short rotation coppice results to willow in certain studies but could also have potential in short rotation forestry. It was noted that over just three growing seasons P. elongata varieties could achieve 92 kg/tree and in plantation strategies using 2000 trees per hectare, 150–300 tonnes/year was produced 5–7 years after planting.
Return to crops overview
Relevant research
Jakubowski, M. (2022). Cultivation Potential and Uses of Paulownia Wood: A Review. Forests, 13(5), 668.
Yadav, N. K., Vaidya, B. N., Henderson, K., Lee, J. F., Stewart, W. M., Dhekney, S. A., & Joshee, N. (2013). A review of Paulownia biotechnology: A short rotation, fast growing multipurpose bioenergy tree. American Journal of Plant Sciences, 4(11), 2070.
Poplar
Populus spp
P. nigra, P. deltoides, P. maximowiczii and P. trichocarpa, P. tremula
General info
Poplar (Populus spp.) belong to the family Salicaeae and are native to the Northern hemisphere. Poplar is among the fastest growing of temperate trees and is therefore of considerable interest as a bioenergy crop.The plant grows to a height of 15–50m with a trunk diameter of 2.5m. Once established, poplar can beharvested every 2-5 years over a life span of over 20 years. Poplar is a multipurpose crop with several environmental benefits such as reducing erosion, phytoremediation of contaminated soils, windbreaks, and biodiversity.
Cultivation and agronomy
Poplar is suited to most soil types including clay, sand, loam, and humus soils. It grows particularly well on well drained and fertile loam with a wide range pH of 5-8. Poplar can be grown as a Short Rotation Forestry(SRF) or Short Rotation Coppice (SRC). The plant can grow up to about 1.5m in height during the first yearand from 3-5m for each of the following years depending on the cultivar, site conditions, spacing andmanagement practices. For large scale plantations, it is recommended to plant mixtures of poplar varieties with about 100 trees of a single cultivar in each block, and different cultivars in neighbouring blocks.
If considering mechanised harvesting, plant at a spacing of 0.6m apart in twin rows with 0.75m between rowsand a 1.5m alley between each twin-row. Poplar can be planted in densities of 1,500 up to 1,800 trees per hectare for bioenergy purposes. Yields of 20-25m3 of wood/ha/yr is achievable in the UK. Young growth is attractive to deer, hare, and rabbits. Appropriate fencing may be required in areas where these animals areprevalent. Common pests includes the small poplar leaf beetle (Phratora vitellinae), and the large leaf beetle (Chrysomela populi).
Return to crops overview
Relevant research
Clifton‐Brown, J., Harfouche, A., Casler, M. D., Dylan Jones, H., Macalpine, W. J., Murphy‐Bokern, D., … & Lewandowski, I. (2019). Breeding progress and preparedness for mass‐scale deployment of perennial lignocellulosic biomass crops switchgrass, miscanthus, willow and poplar. Gcb Bioenergy, 11(1), 118-151.
Biomass Connect Trials
Poplar is being grown as both SRC and SRF as part of the Biomass Connect trials at the following hub sites:
- AFBI Hillsborough
- BGI Chesham
- IBERS Aberystwyth
- NIAB Headley Hall
- Newcastle University Cockle Park Farm
- Rothamsted Research North Wyke
- SRUC Ayrshire
- SRUC Edinburgh
For the Biomass Connect SRF Trials, we planted 3 varieties:
- A4A (P. deltoides × P. nigra) Italian (Female)
- AF7 (Populus ?) Italian (Male) Unsure of this pedigree
- Vesten (Populus deltoides × Populus nigra) Belgian (Female)
For the Biomass Connect SRC Trials, we planted 6 varieties:
- A4A (P. deltoides × P. nigra) Italian (Female)
- AF7 (Populus ?) Italian (Male) Unsure of this pedigree
- Vesten (P. deltoides × P. nigra) Belgian (Female)
- AF2 (P. deltoides × P. nigra) Italian (Male)
- Muur (P. deltoides × P. nigra) Belgian (Male)
- Oudenburg (P. deltoides × P. nigra) Belgian (Female)
Willow
Salix spp.
General info
Willow is one of the most popular short rotation coppicing species for energy crop utilisation, it is a pioneer species that establishes well in new environments with rigorous juvenile growth. It comprises over 400 species worldwide with around 10% of these being deciduous tree species and most being multiple stemmed trees and shrubs.
Due to popularity and success, there are >50 willow cultivars registered with the Community Plant Variety Office (CPVO) with more the 25 commercially available in the UK. Commercial varieties provide benefits including increased rust resistances and increased yields compared to wild varieties due to targeted enhancements. Key willow species for bio-energy production in the UK tend to originate from northern temperate species as they can largely deal with the range of temperatures faced in the UK.
Cultivation and agronomy
Willow can be harvested on 2–5-year rotations at densities up to 15,000 plants per hectare depending on the productivity of the site and the environmental conditions. Planted willow can remain viable for 15–30 years and has a rapid growth rate achieving 6–8 metre heights between each rotation of cutting (depending on rotation year strategy employed).
Generally, willow is adaptable to a range of soils and conditions, however dry sandy soils may struggle to supply sufficient moisture for efficient growth, and organic peat heavy soils may cause too much competitive weed impacts to make the growth strategy efficient. Willow coppices need more water than any other conventional agricultural crop therefore areas of high rainfall are extremely beneficial.
Despite the temperate adaptability of most willow species for higher productivity rates it is recommended that plantation sites be below 100m above sea level. It has been shown that Willow harvesting yields equated to 5–14 oven dried tonnes ha-1 y-1 across several studies, with 1 hectare supply of willow woodchip providing energy roughly equivalent 4,500 litres of home heating oil (depending on moisture levels of willow biomass and productivity of a given hectare per year etc).
Commercially, willow propagation involves the planting of winter-dormant stem cuttings in the spring. Mechanical planting is performed whereby cut stem sections from willow whips are inserted into prepared soils. Following the first growing season cutbacks are performed to around 10cm above ground level to encourage the formation of multi stemmed stools for increased productivity benefits.
Return to crops overview
Relevant research
Clifton‐Brown, J., Harfouche, A., Casler, M. D., Dylan Jones, H., Macalpine, W. J., Murphy‐Bokern, D., … & Lewandowski, I. (2019). Breeding progress and preparedness for mass‐scale deployment of perennial lignocellulosic biomass crops switchgrass, miscanthus, willow and poplar. Gcb Bioenergy, 11(1), 118-151.
Biomass Connect Trials
SRC willow is currently being grown as part of the Biomass Connect trials at the following hub sites:
- AFBI Hillsborough
- BGI Chesham
- IBERS Aberystwyth
- NIAB Headley Hall
- Newcastle University Cockle Park Farm
- Rothamsted Research North Wyke
- SRUC Ayrshire
- SRUC Edinburgh
We also have a willow varieties trail at the following hub sites:
Additional Resources from Biomass Connect
Read our Willow Factsheet
More Resources

Read the growers guide to short rotation coppice willow varieties for biomass publication from the AWBD Project.



















